How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both recreational and professional users. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover essential safety procedures, legal considerations, and troubleshooting tips to ensure a smooth and enjoyable flight experience, regardless of your skill level.
We will explore the fundamental aspects of drone technology, including different drone types, their functionalities, and the importance of understanding the various components. This will lay a strong foundation for learning the essential controls and maneuvers necessary for safe and confident flight. We’ll also cover advanced techniques for achieving professional-quality footage, including camera settings, flight planning, and post-processing considerations.
Finally, we’ll discuss the legal and regulatory frameworks surrounding drone operation to ensure compliance and responsible flying practices.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the different parts of your drone and the terminology used is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will cover the key components and provide a glossary of common terms.
Drone Components and Their Functions
A drone consists of several interconnected components working in harmony. Let’s explore each one’s role.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust needed for flight. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation. Brushless motors are common in modern drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: This is the drone’s “brain,” responsible for processing data from various sensors and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands. It integrates data from the GPS, IMU, and other sensors.
- Battery: Provides the electrical power to run the motors and other onboard electronics. The flight time is directly related to the battery’s capacity.
- GPS: A Global Positioning System receiver allows the drone to determine its location and maintain its position, crucial for autonomous flight and features like Return-to-Home.
- Camera: Captures photos and videos. Features vary greatly depending on the drone model, from basic cameras to high-resolution models with advanced features like 4K video recording and gimbal stabilization.
Glossary of Common Drone Terms
Here’s a quick guide to some common terms you’ll encounter.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures the drone’s orientation and movement using accelerometers and gyroscopes.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mount for the camera, helping to keep footage smooth and stable even during flight.
- Firmware: The software that controls the drone’s hardware and functions. Updates are often released to improve performance and add features.
- Payload: The weight carried by the drone, including the camera and any other attached equipment.
- Range: The maximum distance a drone can fly from the controller before losing signal.
- RTF (Ready-To-Fly): A drone that comes fully assembled and ready to fly out of the box.
Comparison of Drone Battery Types
Different battery types offer various advantages and disadvantages.
| Battery Type | Voltage (V) | Typical Capacity (mAh) | Approximate Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo (Lithium Polymer) | 3.7-14.8 | 500-5000+ | 10-30+ |
| LiHV (Lithium Polymer High Voltage) | 3.8-15.2 | 500-5000+ | 10-35+ (generally longer than LiPo) |
| LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | 3.2-12.8 | 500-5000+ | 10-30+ (generally less flight time compared to LiPo and LiHV) |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring a safe and successful flight. This involves both checking the drone’s components and understanding safe operating procedures.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, perform the following checks:
- Inspect propellers for damage or cracks.
- Check battery level and ensure it’s properly connected.
- Verify GPS signal strength.
- Calibrate the compass if needed.
- Ensure sufficient space and clear surroundings.
- Check local regulations and weather conditions.
Safe Drone Operation Practices
Adhering to safe practices is paramount for preventing accidents and ensuring responsible drone operation.
- Maintain a safe distance from people and obstacles.
- Avoid flying near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Never fly beyond visual line of sight (VLOS).
- Be aware of surrounding environment and potential hazards (power lines, trees, etc.).
- Fly responsibly and consider the impact on others.
Safe Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight process can be helpful. A flowchart would show a sequential process, starting with battery check, moving to propeller inspection, GPS signal verification, and ending with a final confirmation before takeoff.
Basic Drone Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the basic controls is the first step to successfully operating your drone. This section will cover the controls and fundamental maneuvers.
Drone Transmitter Controls
Most drone transmitters have two joysticks. One typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the other controls forward/backward and left/right movement.
- Left Stick: Generally controls throttle (altitude) and pitch (forward/backward).
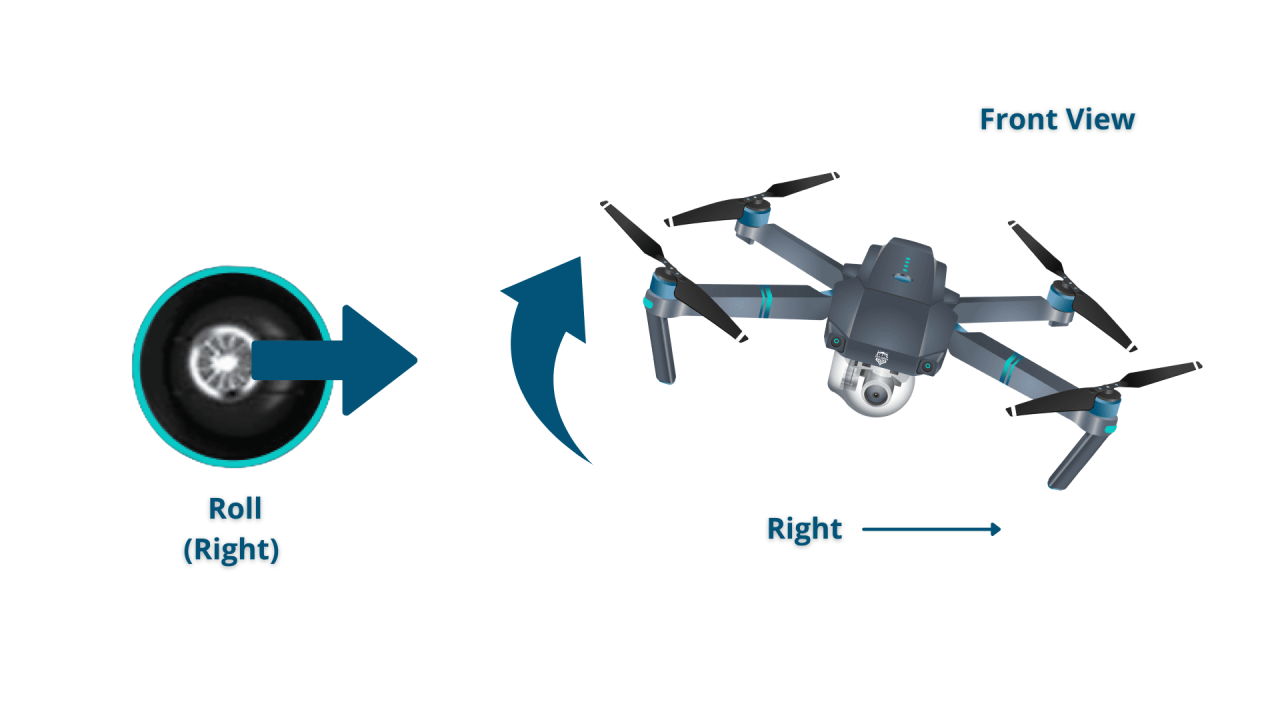
- Right Stick: Generally controls yaw (rotation) and roll (left/right movement).
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Here’s a step-by-step guide to performing basic maneuvers.
- Takeoff: Gently push the left stick upwards.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady position by carefully adjusting the left stick.
- Landing: Gently lower the left stick.
- Moving Forward/Backward: Push the left stick forward or backward.
- Moving Left/Right: Push the right stick left or right.
- Rotating: Rotate the right stick to turn the drone.
Common Drone Control Errors and Avoidance
Understanding common mistakes can help prevent accidents.
- Sudden movements: Avoid abrupt joystick movements, which can lead to loss of control.
- Ignoring battery level: Always monitor the battery level and land before it gets too low.
- Flying in strong winds: Avoid flying in high winds, which can make control difficult.
- Flying too close to obstacles: Maintain a safe distance from obstacles to prevent collisions.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can explore more advanced techniques for improved control and footage quality.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions requires careful adjustments to maintain stability. It’s important to understand wind direction and strength and adjust control inputs accordingly.
Achieving Smooth and Stable Footage
Smooth footage requires steady hand control and potentially the use of a gimbal. Practice smooth, controlled movements to minimize jerky camera motion.
Advanced Maneuvers
Depending on the drone model, advanced maneuvers such as flips and rolls might be possible. These require practice and careful execution.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding your drone camera’s settings is crucial for capturing high-quality photos and videos. This section covers camera settings and shooting modes.
Drone Camera Settings, How to operate a drone
Typical drone camera settings include aperture, shutter speed, and ISO.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera.
- Shutter Speed: Controls how long the sensor is exposed to light.
- ISO: Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Utilizing different shooting modes and understanding the interplay of camera settings will allow for better results.
- Use different shooting modes: Experiment with different shooting modes like video, photo, timelapse, and panorama.
- Adjust settings for different lighting conditions: Adjust settings such as aperture, shutter speed, and ISO to optimize image quality based on the lighting.
- Use a gimbal for smooth footage: Employ a gimbal to stabilize the camera for smoother videos.
Comparison of Image/Video Formats
Various image and video formats offer different advantages and disadvantages.
| Format | Pros | Cons | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG | Smaller file size, widely compatible | Lower image quality compared to RAW | Quick sharing and viewing |
| RAW | Higher image quality, more editing flexibility | Larger file size, requires specialized software | Professional photography, post-processing |
| MP4 | Widely compatible, good balance of quality and file size | Can be large depending on resolution and bitrate | General video recording |
| MOV | High quality, good for professional video editing | Larger file size | Professional video production |
Drone Flight Planning and Mission Setup: How To Operate A Drone
Planning your flight path in advance can improve safety and efficiency. This section covers flight planning software and autonomous missions.
Flight Path Planning Software
Many software applications are available to plan flight paths, set waypoints, and automate drone missions. These applications often include features for obstacle avoidance and battery life optimization.
Setting Up Waypoints and Autonomous Missions
Waypoints are pre-defined points in a flight path. By setting waypoints, you can create autonomous missions where the drone flies a specific route without manual control.
Optimizing Battery Life During Long Flights

For extended flights, optimizing battery life is crucial. This includes planning shorter flight segments, using efficient flight patterns, and choosing the appropriate battery.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This section covers cleaning, maintenance, and troubleshooting common problems.
Drone Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance can extend the life of your drone. This includes cleaning the propellers, body, and camera lens, as well as inspecting for any damage.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and efficient drone operation.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Understanding common problems and their solutions can save time and frustration. Some common issues include battery problems, motor malfunctions, and GPS signal loss.
Essential Drone Maintenance Tools
Having the right tools for maintenance can simplify the process and prevent damage. Essential tools include a cleaning kit, propellers, and potentially a multi-tool.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone legally and responsibly is essential. This section covers regulations, permits, and airspace restrictions.
Legal Regulations and Restrictions
Drone regulations vary by region and country. It’s crucial to understand the specific rules and regulations in your area before flying.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
In some cases, obtaining permits or licenses may be required before operating a drone, especially for commercial use or in restricted airspace.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Certain areas are restricted airspace, such as airports and military bases. It’s important to check for no-fly zones before flying.
Drone Photography and Videography Composition
Achieving visually appealing drone footage requires understanding basic composition techniques. This section covers framing, angles, and composition techniques.
Best Practices for Framing Shots
Proper framing is essential for creating visually appealing drone footage. Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other composition techniques.
Different Camera Angles and Perspectives
Different camera angles can drastically alter the mood and impact of your footage. Experiment with various angles, such as high-angle shots, low-angle shots, and tracking shots.
Composition Techniques for Stunning Aerial Photography
To achieve stunning aerial photography, utilize techniques like the rule of thirds, leading lines, symmetry, and patterns.
- Rule of Thirds
- Leading Lines
- Symmetry and Patterns
- Framing
- Perspective
Emergency Procedures and Safe Recovery
Knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. This section covers emergency procedures, safe recovery, and the Return-to-Home function.
Handling Emergency Situations

In case of emergencies like signal loss or low battery, it’s crucial to follow established procedures for safe recovery. This may include attempting to regain control, activating the Return-to-Home function, or performing a controlled emergency landing.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to help you get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This guide covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers, ensuring you’re well-prepared for a safe and enjoyable drone experience.
Mastering the art of drone operation takes practice, but with the right resources, it’s achievable.
Safely Recovering a Crashed Drone
If your drone crashes, approach the situation carefully to prevent further damage or injury. Inspect for damage before attempting to power it on.
Using the Return-to-Home Function Effectively
The Return-to-Home (RTH) function automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point. Ensure the GPS signal is strong before relying on RTH.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a solid foundation, equipping you with the essential skills and safety awareness needed to confidently navigate the skies. Remember, consistent practice and adherence to safety regulations are paramount. As you progress, explore advanced techniques and continue to refine your skills to capture breathtaking aerial perspectives and unlock the full potential of your drone.
Essential FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Beginner-friendly drones typically feature user-friendly interfaces, GPS stabilization, and return-to-home functions. Look for models with obstacle avoidance capabilities for added safety.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, or even longer with larger batteries.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If signal is lost, the drone will automatically attempt to return to its takeoff point. However, always fly within visual line of sight whenever possible.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and registration procedures in your area.
